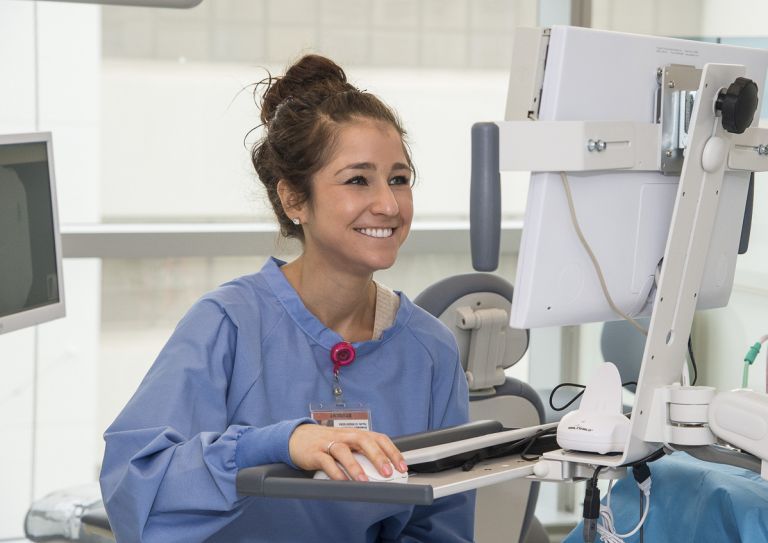
The Clinical Medical Assistant + Electronic Health Records Specialist Certificate is a comprehensive National Healthcareer Association (NHA)-certified course bundle to train you for one of today’s fastest growing careers. Upon completion, you will be eligible to sit for the NHA’s CEHR and CCMA certification exams. This course includes a voucher which covers the fee of the exam. You will also have the opportunity to gain access to our Externship Starter Kit.
In the first course, you will learn how medical law, ethics, and HIPAA rules factor into a clinical medical assistant’s work. In addition, you will be trained to use scheduling systems, facilitate patient check-in and check-out, assess medical record, administer injections, and more. You will also study body systems and their main functions, so you can assist with patient exams.
The second part of the bundle will train you in electronic health record (EHR) systems. You will learn how staff members and patients interact with EHR systems, what benefits these systems provide, and the steps to implementing an electronic health record system.
This program is offered by our partner, ed2go. It is entirely online and is completed at your own pace. When you register, you receive twelve (12) months to complete this program.
Date: Open enrollment. Start anytime — up to 12 months to complete.